|
Author Ashley Davidoff MD
Assisted by Charlie Allison MD Scott Tsai MD Adam Asarch MS II Sam Yam PhD David Lee MD
Masses in the Pancreas – a pictorial differential diagnosis
Approach
Decide whether the lesion is cystic solid, or combination, and then look for associated findings to narrow the differential diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis
Solid masses
pancreatic neoplasms
adenocarcinoma –
most common, usually head, 1-2%- 1 yr survival
cystadenoma
serous cystadenoma
benign, female, tiny cysts, (but may be up to 2cms) large tumor, may be head body or tail, central stellate scar, +/- calcification
mucinous cystadenoma/ cystadenocarcinoma
benign, premalignant, or malignant, female++, large (mean 12cms) thick septations, 85% tail and body, scattered dystrophic calcification
islet cell tumors
insulinoma (beta-cell) usually solitary, 85% benign
gastrinoma small, slow-growing, multiple, 60% malignant
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome: mult. intractable ulcers
VIPoma – vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)
WDHA syndrome: watery diarrhea, hypokalemia, achlorhydria
Verner-Morrison syndrome
glucagonoma hyperglycemia, migratory necrolytic erythema
lymphoma
soft-tissue tumors (rare)
metastases (breast, lung, melanoma, stomach, colon)
syndromes
von Hippel-Lindau
Cystic masses
pseudocysts
acute pancreatitis
blunt abdominal trauma
surgery
idiopathic
cystic neoplasms
slow-growing
more common in women
syndromes
von Hippel-Lindau
Solid masses of the pancreas
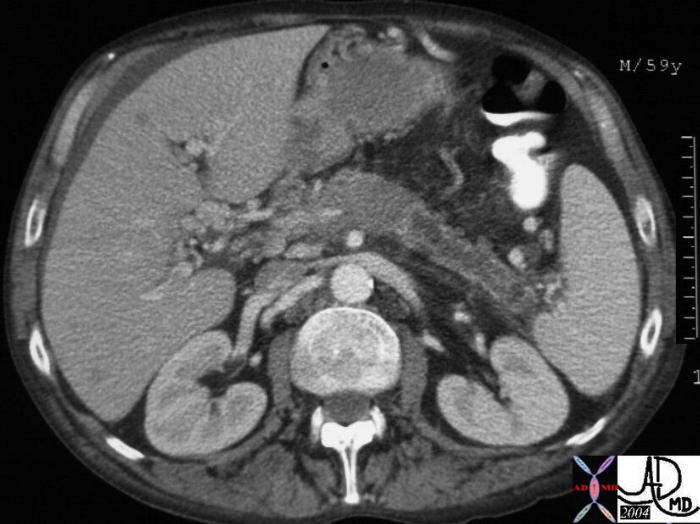 Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas |
| This CT scan through the pancreas shows a mass in the neck associated with pancreatic duct dilatation and secondary atrophy in the pancreatic tail. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of a primary carcinoma of the pancreas. Based on the desmoplastic nature of the process the tumor is most likely an adenocarcinoma. 30101a05 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
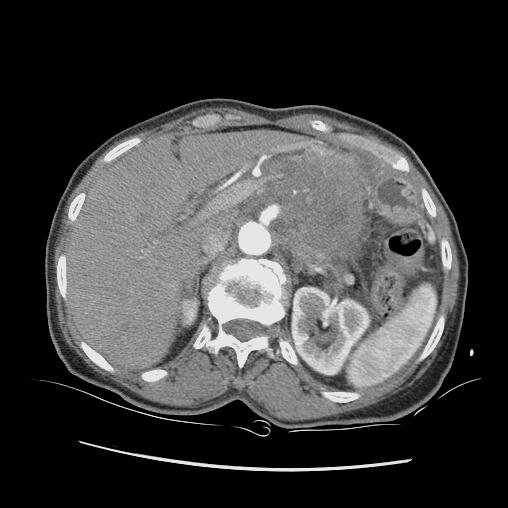 Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas |
| This CT scan through the pancreas shows a mass in the body of the pancreas associated with encasement of the portal vein and splenic artery ((subtotal occlusion) with an almost complete encirclement of the celiac axis by a necklace of aggressive tissue. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of a primary carcinoma of the pancreas. Based on the desmoplastic nature of the process the tumor is most likely an adenocarcinoma. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD18103 |
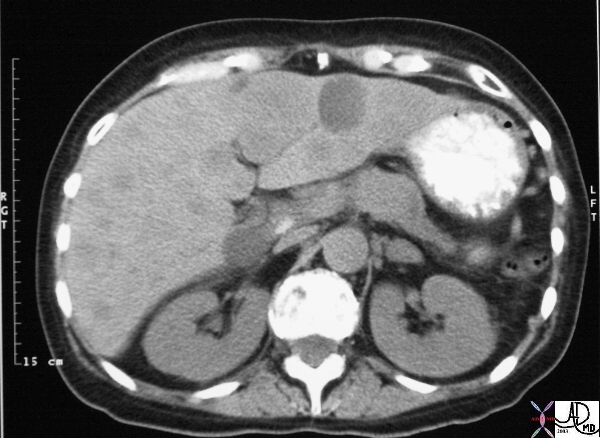 Malignant Gastrinoma of the Pancreas Malignant Gastrinoma of the Pancreas |
| This CT scan through the pancreas shows a mass in the body of the pancreas associated with metastatic liver disease. The patient presented with Cushingoid features which was associated with ectopic ACTH biochemistry. An adremnal nodule is noted reflective of hyperplasia from the effect of ACTH. The mass at autopsy was consistent with a malignant gastrinoma associated with ectopic ACTH production. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 19859 |
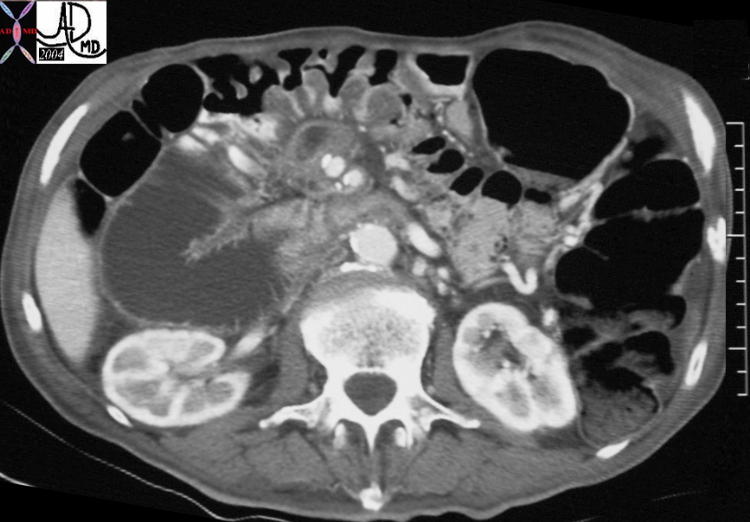 Carcinoma of the Pancreas Carcinoma of the Pancreas |
| This CT scan through the pancreas shows a small mass in the uncinate process of the pancreas associated with a dilated and obstructed duodenum. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of a primary carcinoma of the pancreas. Based on the desmoplastic nature of the process the tumor is most likely an adenocarcinoma. 20601 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
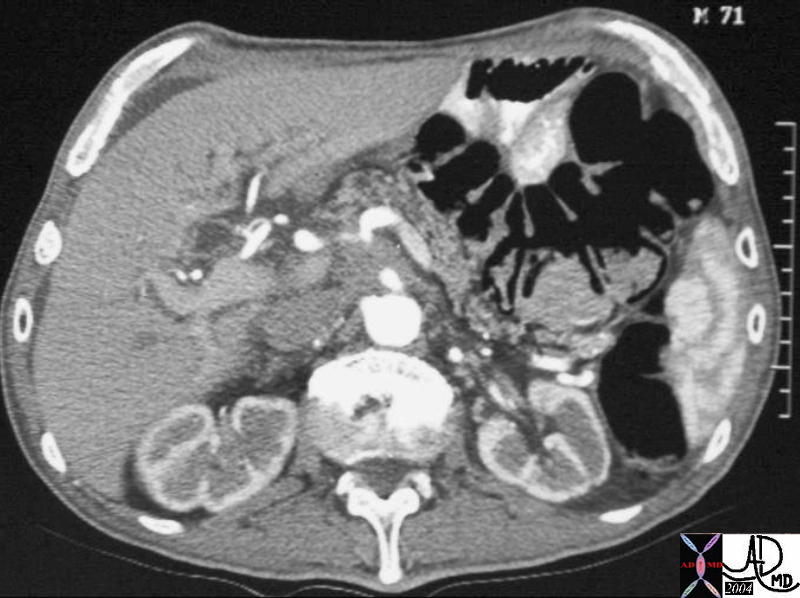 Carcinoma of the Pancreas Carcinoma of the Pancreas |
| This CT scan through the pancreas shows a small mass in the uncinate process of the pancreas associated with encasement of the celiac axis and a dilated CBD. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of a primary carcinoma of the pancreas. Based on the desmoplastic nature of the process the tumor is most likely an adenocarcinoma. 20599 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
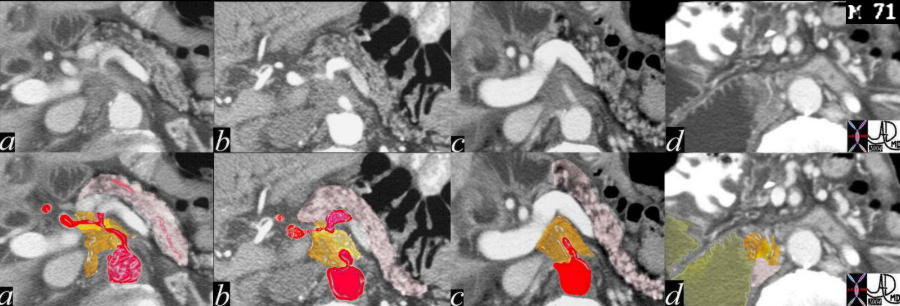 Carcinoma of the Pancreas Carcinoma of the Pancreas |
| This CT scan through the pancreas is a series with overlay from the above case, and shows a small mass in the uncinate process of the pancreas associated with encasement of the celiac axis and SMA, with a dilated CBD. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of a primary carcinoma of the pancreas. Based on the desmoplastic nature of the process, the tumor is most likely an adenocarcinoma. 20607c06 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
 Carcinoma of the Tail of the Pancreas Carcinoma of the Tail of the Pancreas |
| This CT scan through the pancreas shows a mass in the tail of the pancreas associated with splenic invasion ascites, a probably liver metastasis, and thickened omentum. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of a primary carcinoma of the pancreas, with metastatic disease. 20796 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
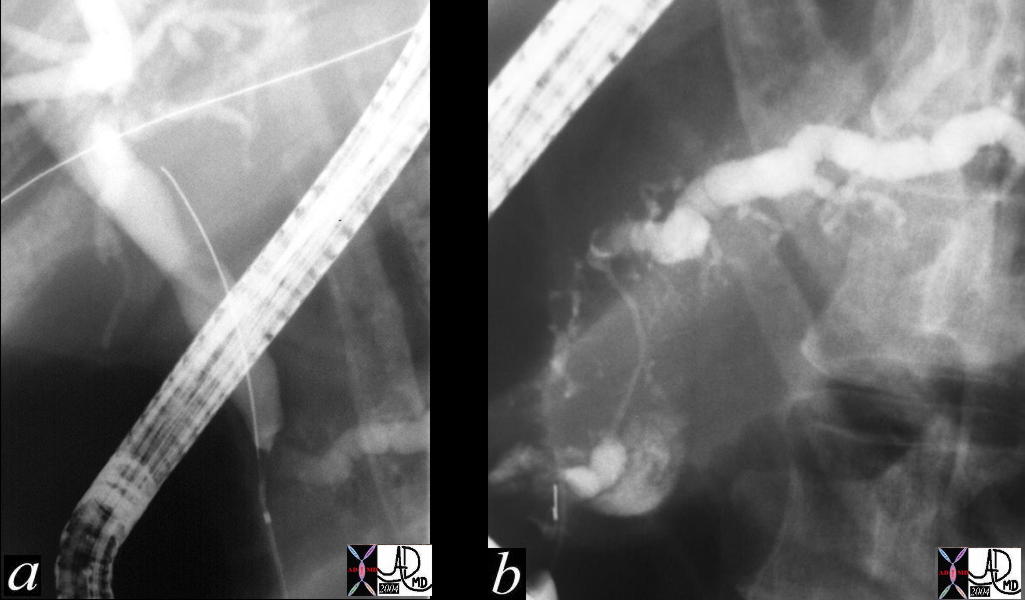 Double Duct Sign Double Duct Sign |
| This ERCP shows a double duct sign with a dilated CBD and pancreatic duct. These findings are consistent with a primary adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Chronic pancreatitis is a remote possibility. 31062c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
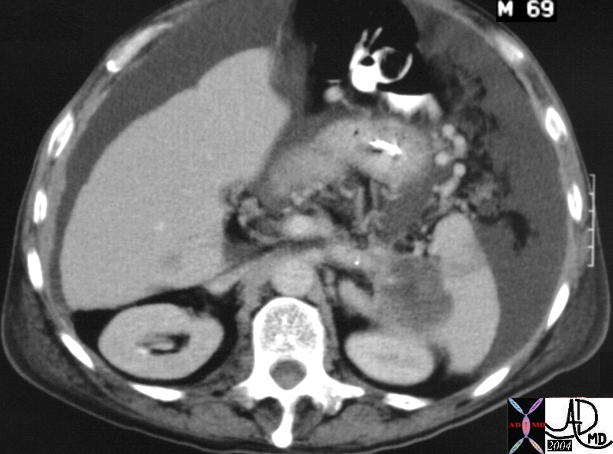
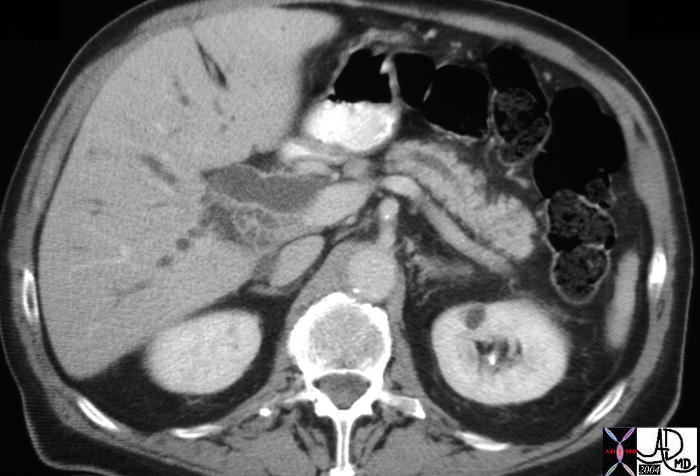 Double Duct Sign Double Duct Sign |
| This CT scan through the pancreas shows a dilated pancreatic duct and a dilated CBD (“double duct” sign). These findings are consistent with a primary adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Chronic pancreatitis is a remote possibility. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of a primary carcinoma of the pancreas. 40837 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
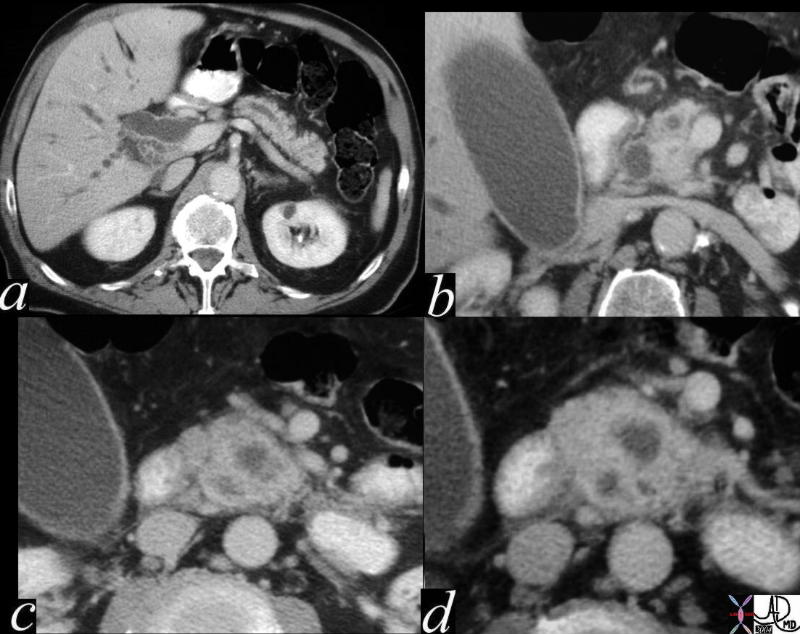 Double Duct Sign Double Duct Sign |
| This CT scan series of the above case through the pancreas shows the mass in the head of the pancreas, (c,d) a dilated pancreatic duct and a dilated CBD (“double duct” sign). These findings are consistent with a primary adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. 40840c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
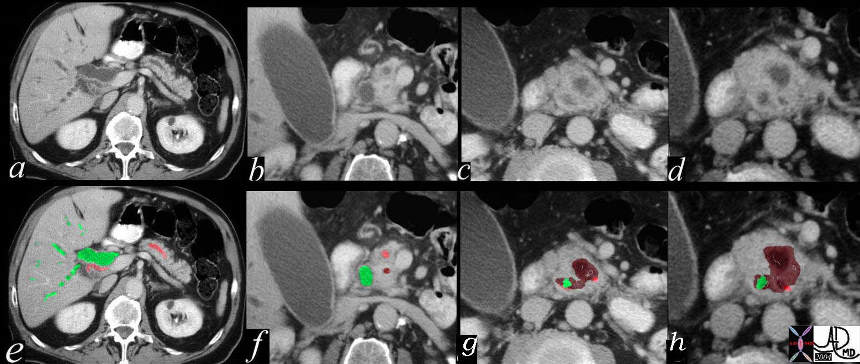 Double Duct Sign Double Duct Sign |
| This CT scan series of the above case through the pancreas shows the findings described in overlay. The mass is maroon, the CBD in green and the pancreatic duct in pink. 40840c02 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
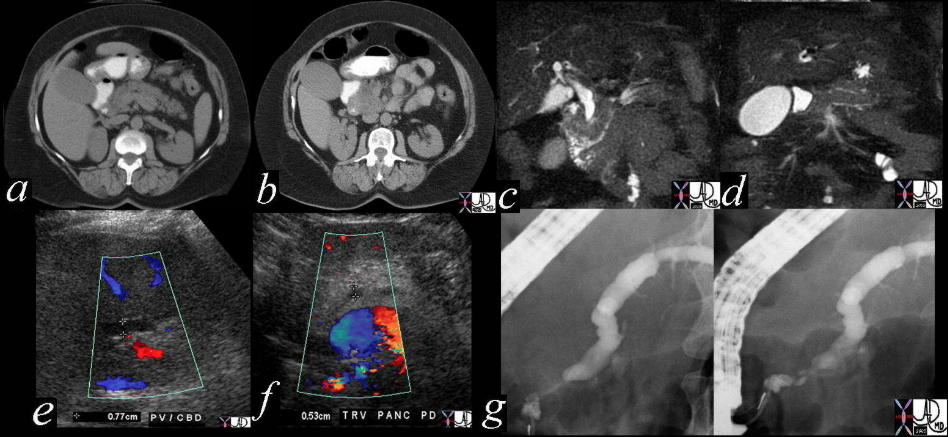 Double Duct Sign Double Duct Sign |
| The CTscan MRI, US and ERCP of the pancreas shows a dilated pancreatic duct and a dilated CBD (“double duct” sign). These findings are consistent with a primary adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. 41293a16c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
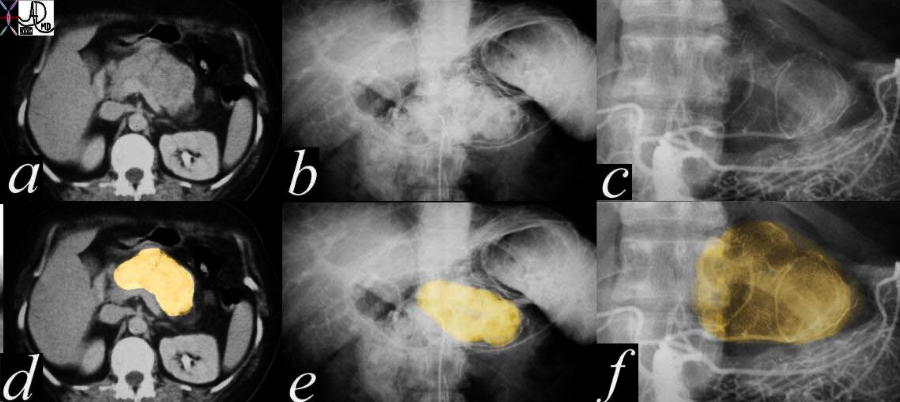 Microcystic Form Microcystic Form |
| This is a series of images from a middle aged female with a hypervascular mass in the body of the pancreas. Since adenocarcinoma of the pancreas tends to be hypovascular it is unlikely that the histological type is the common form. In this case the diagnosis was a micronodular carcinoma 40640c02 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
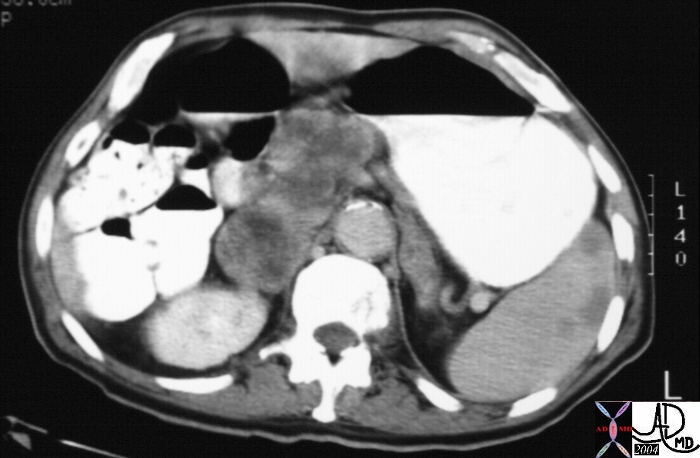 This CT scan through the head of the pancreas shows large complex mass in the head of the pancreas, associated with an adrenal mass, and multiple masses in the spleen. These findings are consistent with metastatic carcinoma. The patient had a known primary carcinoma of the lung. 20644 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the head of the pancreas shows large complex mass in the head of the pancreas, associated with an adrenal mass, and multiple masses in the spleen. These findings are consistent with metastatic carcinoma. The patient had a known primary carcinoma of the lung. 20644 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
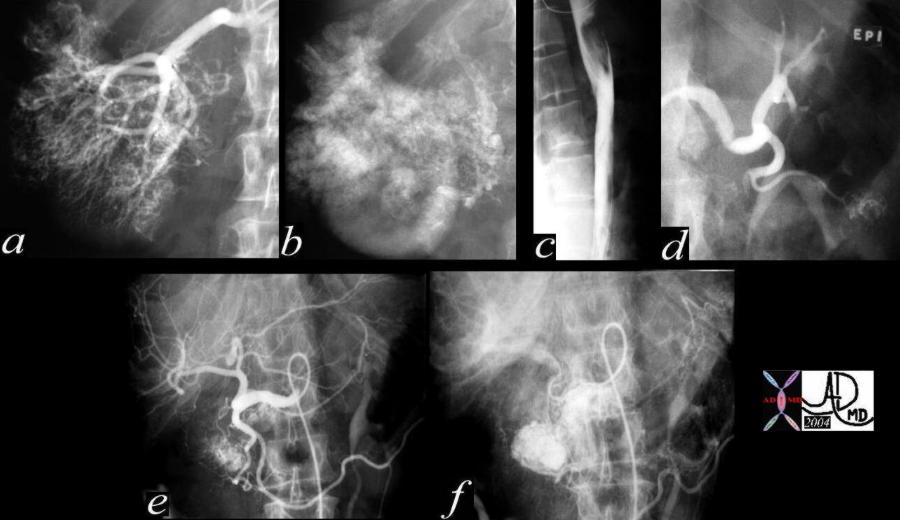 This angiogram shows a hypervascular mass in the right kidney consistent with an RCC(a,b), with extension into the IVC (b,c) A second mass that does not respond to intraarterial epinephrine in the left kidney is consistent with a second RCC (d) A hypervascular mass in the head and uncinate process with secondary portal hypertension from A-V shunting reflects a metastatic RCC to the pancreas (e,f). 40437c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This angiogram shows a hypervascular mass in the right kidney consistent with an RCC(a,b), with extension into the IVC (b,c) A second mass that does not respond to intraarterial epinephrine in the left kidney is consistent with a second RCC (d) A hypervascular mass in the head and uncinate process with secondary portal hypertension from A-V shunting reflects a metastatic RCC to the pancreas (e,f). 40437c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
Cystic Masses of the Pancreas
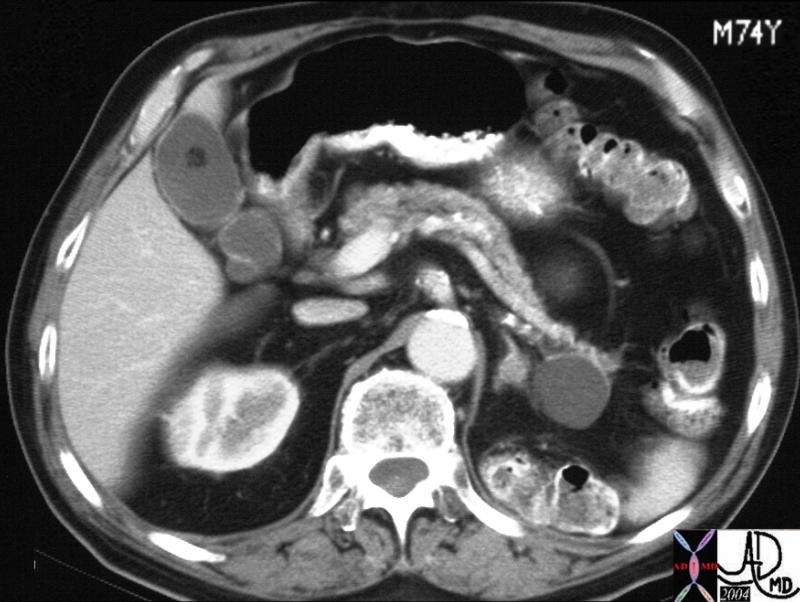 This CT scan through the pancreas shows a cystic mass in the pancreatic tail associated with surgical absence of the left kidney, a left adrenal nodule and a cholesterol gall stone. Prior surgery with iatrogenic trauma to the tail of the pancreas is the most likely cause of the pseudocyst. The cystic nature needs to be verified by US. 25055 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a cystic mass in the pancreatic tail associated with surgical absence of the left kidney, a left adrenal nodule and a cholesterol gall stone. Prior surgery with iatrogenic trauma to the tail of the pancreas is the most likely cause of the pseudocyst. The cystic nature needs to be verified by US. 25055 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
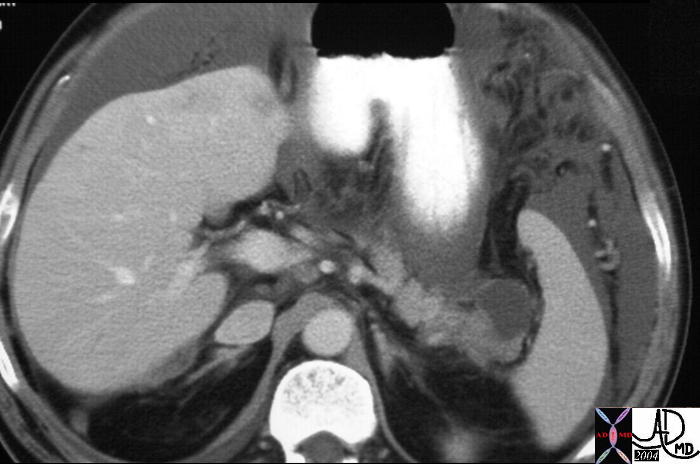 This CT scan through the pancreas shows a cystic mass in the pancreatic tail associated with thickened gastrolienal ligament and ascites. This case represents transperitoneal spread of a known pancreatic carcinoma. Metastatic nodules are also noted in the liver. 20114 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a cystic mass in the pancreatic tail associated with thickened gastrolienal ligament and ascites. This case represents transperitoneal spread of a known pancreatic carcinoma. Metastatic nodules are also noted in the liver. 20114 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
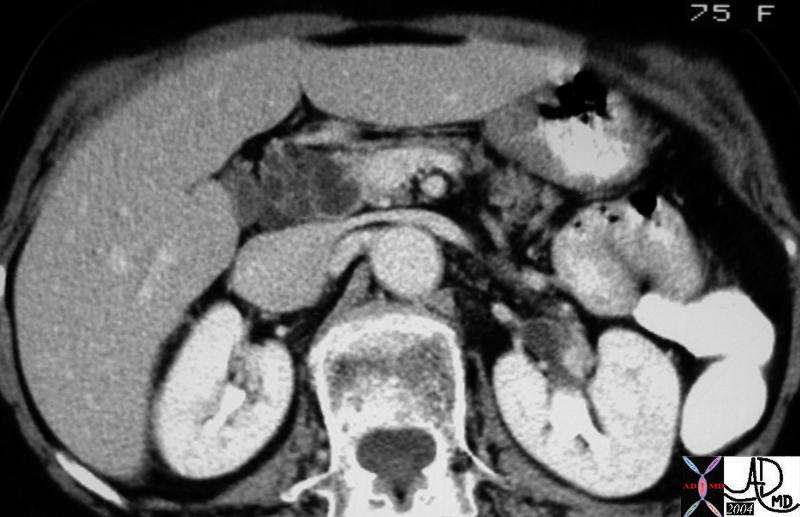 The CTscan through the head of the pancreas is of a 75 year old female with abdominal discomfort. There is a multiloculated cystic mass in the head of the pancreas. The age sex, appearance, and location make a serous cystadenoma most likely. 40585 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD The CTscan through the head of the pancreas is of a 75 year old female with abdominal discomfort. There is a multiloculated cystic mass in the head of the pancreas. The age sex, appearance, and location make a serous cystadenoma most likely. 40585 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
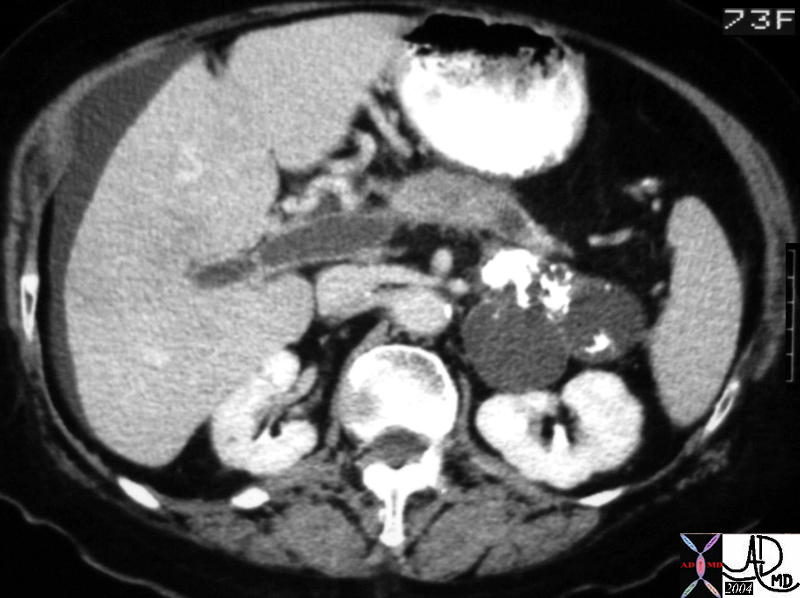
 This CT scan through the pancreas shows a hypodense mass in the pancreatic head, associated with a central dystrophic calcification and a dilated pancreatic duct. These findings are consistent with a cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the dilated duct. The calcifications in the spleen are granulomatous in origin. 19394c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a hypodense mass in the pancreatic head, associated with a central dystrophic calcification and a dilated pancreatic duct. These findings are consistent with a cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the dilated duct. The calcifications in the spleen are granulomatous in origin. 19394c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
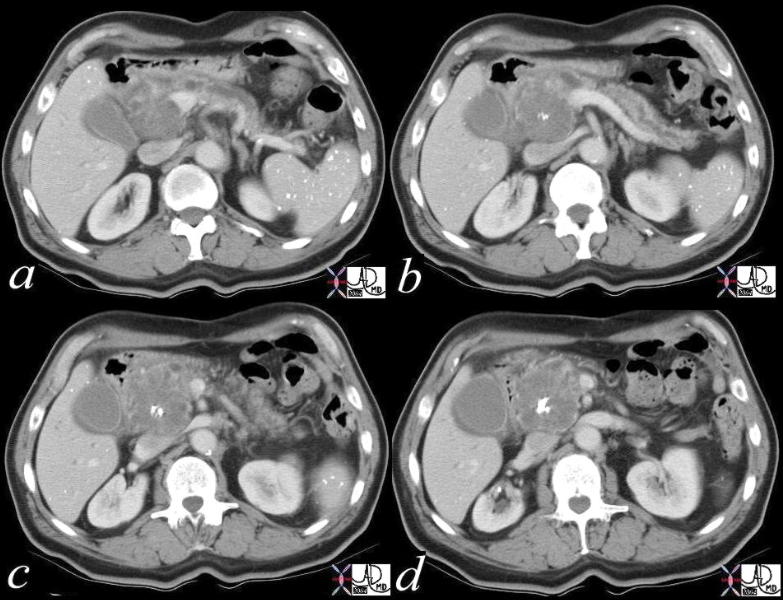
 This CT scan through the pancreas shows a complex cystic mass with dense peripheral dystrophic calcification in the tail of the pancreas. Associated findings include portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and ascites. These findings are consistent with a cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the PVT. An expanded version of this case appears below. 40712 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a complex cystic mass with dense peripheral dystrophic calcification in the tail of the pancreas. Associated findings include portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and ascites. These findings are consistent with a cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the PVT. An expanded version of this case appears below. 40712 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
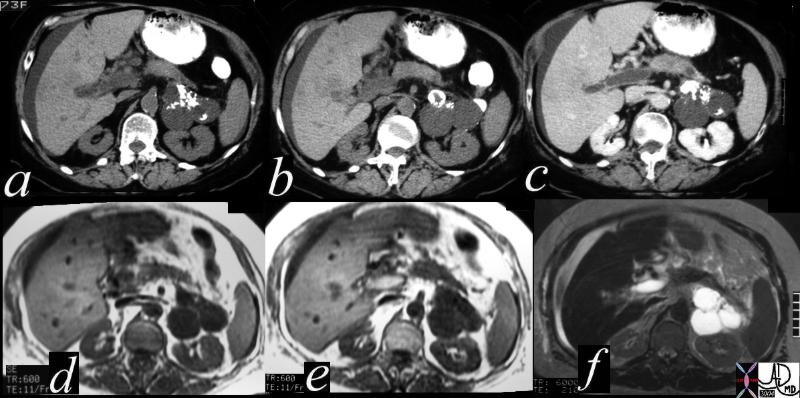 This CT scan through the pancreas (a,b,c) shows a complex cystic mass with dense peripheral dystrophic calcification in the tail of the pancreas. Associated findings include portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and ascites. The lesions on the weighted image (d) are dark, and are bright on the T2 weighted image consistent with their cystic nature. The portal vein is bright on the T1 image and bright on T2 consistent with acute thromus.T2 weighted image (e) reflects the hypointense cystic masses These findings are consistent with a a diagnosis of cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the PVT. 40717c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas (a,b,c) shows a complex cystic mass with dense peripheral dystrophic calcification in the tail of the pancreas. Associated findings include portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and ascites. The lesions on the weighted image (d) are dark, and are bright on the T2 weighted image consistent with their cystic nature. The portal vein is bright on the T1 image and bright on T2 consistent with acute thromus.T2 weighted image (e) reflects the hypointense cystic masses These findings are consistent with a a diagnosis of cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the PVT. 40717c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
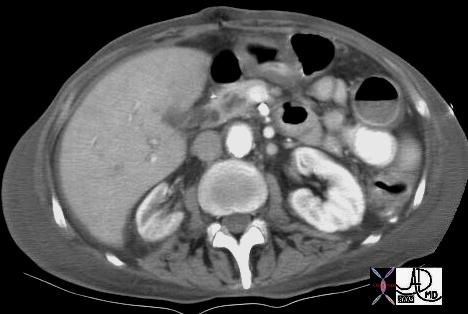 This CTscan through the head of the pancreas shows a small complex and heterogeneous mass, with dominant hypodensity. The anatomic differential diagnosis lies between the duct and the parenchyma. An ERCP was performed 18143 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CTscan through the head of the pancreas shows a small complex and heterogeneous mass, with dominant hypodensity. The anatomic differential diagnosis lies between the duct and the parenchyma. An ERCP was performed 18143 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
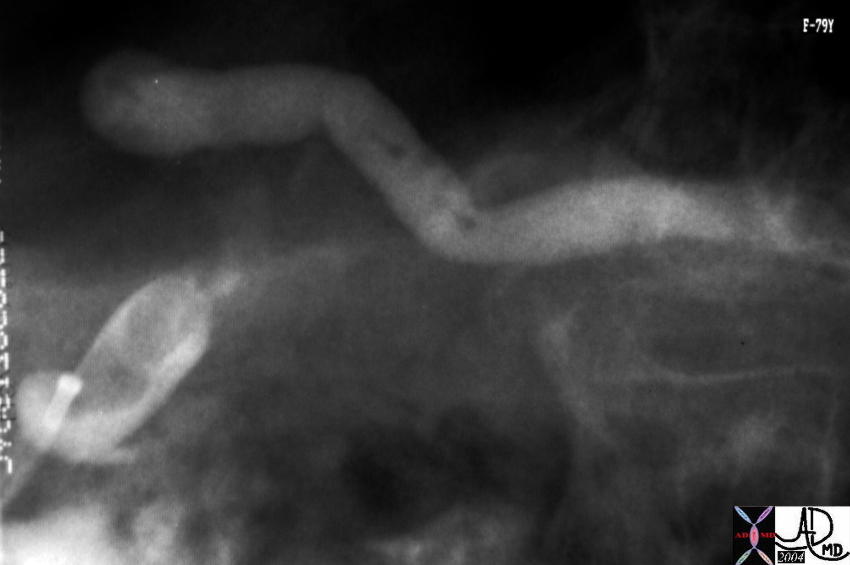 At ERCP mucoid materal was noted in the ampulla. The lesion identified in the uncinate process on the CT was noted as a nodule in the duct. Associated findings included tubular thin filling defects in the duct of the ody consistent with mucus. A diagnosis of mucinous duct ectasia with a papillary tumor with papillary and mucinous features was made at pathology. 40377 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD At ERCP mucoid materal was noted in the ampulla. The lesion identified in the uncinate process on the CT was noted as a nodule in the duct. Associated findings included tubular thin filling defects in the duct of the ody consistent with mucus. A diagnosis of mucinous duct ectasia with a papillary tumor with papillary and mucinous features was made at pathology. 40377 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
 This CT scan through the pancreas shows a large solid mass with vessels that are seemingly not affected by the mass. Associated findings include the retrocrural adenopathy, an aortocaval node and a small amount of ascites. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of lymphoma. 29945 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a large solid mass with vessels that are seemingly not affected by the mass. Associated findings include the retrocrural adenopathy, an aortocaval node and a small amount of ascites. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of lymphoma. 29945 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
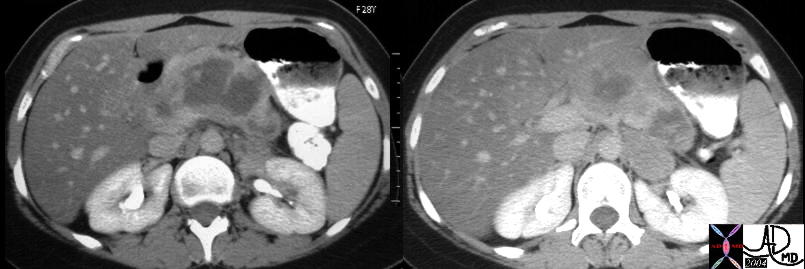 This CT scan through the pancreas of a 28 year old female with known malignancy shows a large solid mass with central low density. She carries a diagnosis non Hodgkin’s lymphoma Associated findings include steatosis of the liver. 40425c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas of a 28 year old female with known malignancy shows a large solid mass with central low density. She carries a diagnosis non Hodgkin’s lymphoma Associated findings include steatosis of the liver. 40425c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
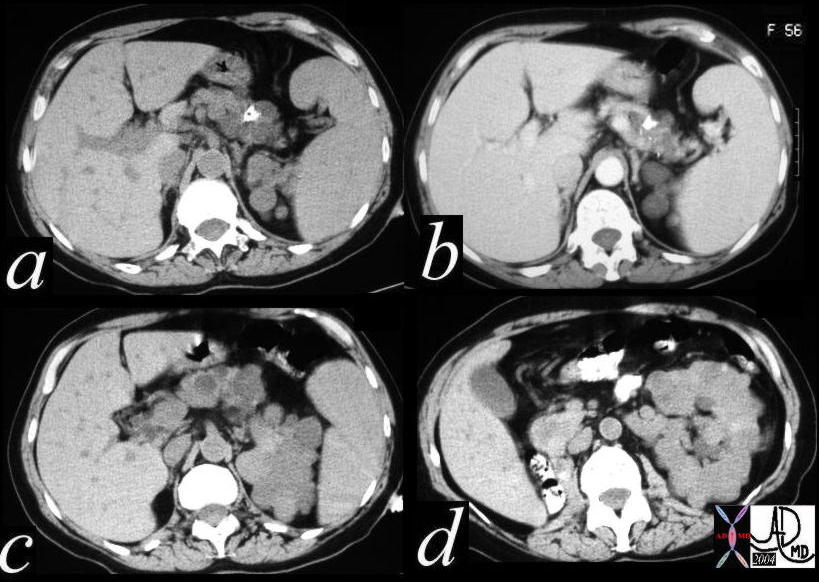 This CT scan through the pancreas shows a complex cystic mass with central calcification in the tail of the pancreas associated with complex masses in the left kidney and surgically absent right kidney. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome with a variety of cystic and solid, benign and malignant tumors of the pancreas and kidney. 40463c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a complex cystic mass with central calcification in the tail of the pancreas associated with complex masses in the left kidney and surgically absent right kidney. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome with a variety of cystic and solid, benign and malignant tumors of the pancreas and kidney. 40463c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
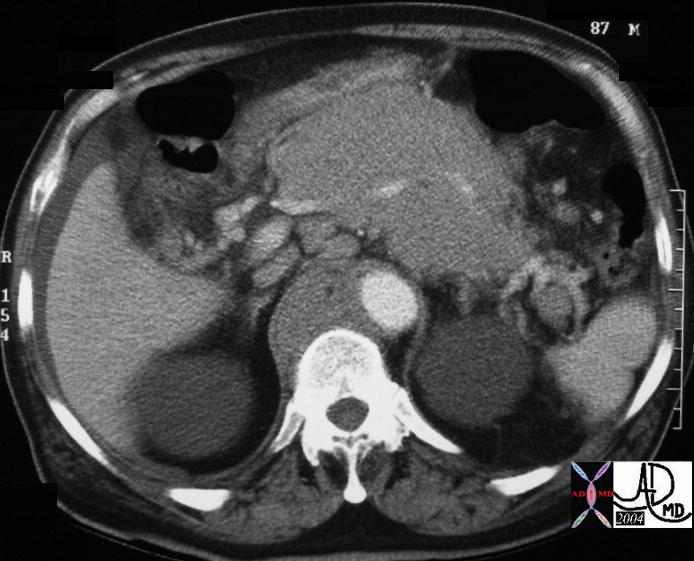
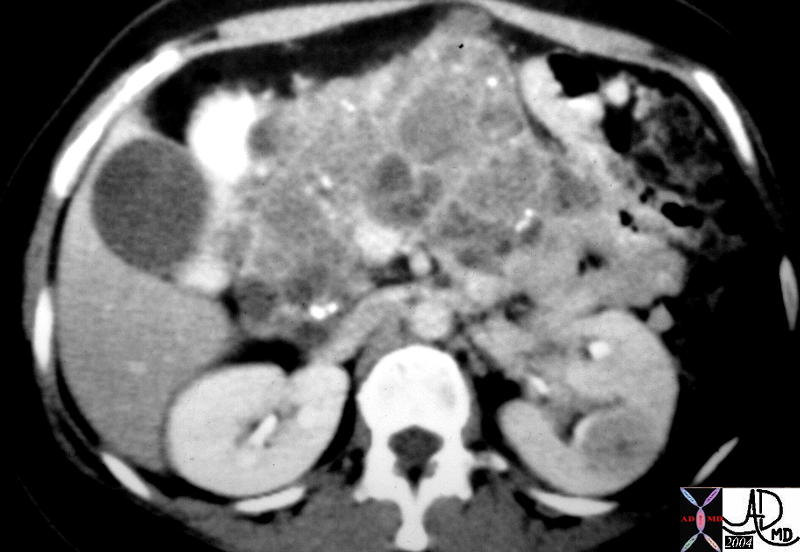 This CT scan through the pancreas shows diffuse heterogeneous enlargement of the pancreas, and a series of complex cystic and solid masses mass with punctate calcifications throughout the whole pancreas. Associated findings include a solid mass in the left kidney. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome with a variety of cystic and solid, benign and malignant tumors of the pancreas 40531 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows diffuse heterogeneous enlargement of the pancreas, and a series of complex cystic and solid masses mass with punctate calcifications throughout the whole pancreas. Associated findings include a solid mass in the left kidney. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome with a variety of cystic and solid, benign and malignant tumors of the pancreas 40531 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
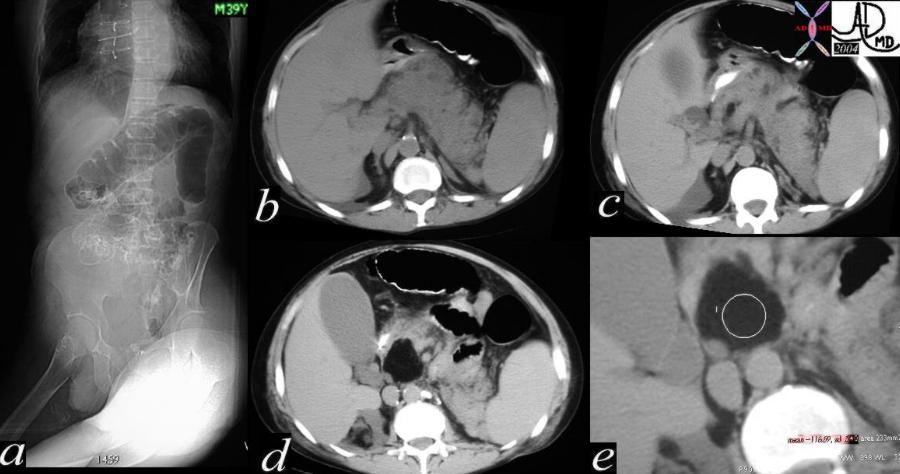 The first image of this series (a), reveals a colon cut off sign and is associated with a mild degree of induration around the pancreas best seen in c. The pancreas itself is enlarged and heterogeneous with a few small complex structures that are too small to resolve, seen best in b and c. A large lipoma is seen in the head of the pancreas in e. The right kidney has a fatty mass in its upper pole consistent with an angiomyolipoma. The overall picture suggests a diagnosis of von Hippel–Lindau syndrome. 40200c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD The first image of this series (a), reveals a colon cut off sign and is associated with a mild degree of induration around the pancreas best seen in c. The pancreas itself is enlarged and heterogeneous with a few small complex structures that are too small to resolve, seen best in b and c. A large lipoma is seen in the head of the pancreas in e. The right kidney has a fatty mass in its upper pole consistent with an angiomyolipoma. The overall picture suggests a diagnosis of von Hippel–Lindau syndrome. 40200c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
|
 Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas
Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas
Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas Malignant Gastrinoma of the Pancreas
Malignant Gastrinoma of the Pancreas Carcinoma of the Pancreas
Carcinoma of the Pancreas Carcinoma of the Pancreas
Carcinoma of the Pancreas Carcinoma of the Pancreas
Carcinoma of the Pancreas Carcinoma of the Tail of the Pancreas
Carcinoma of the Tail of the Pancreas Double Duct Sign
Double Duct Sign Double Duct Sign
Double Duct Sign Double Duct Sign
Double Duct Sign Double Duct Sign
Double Duct Sign Double Duct Sign
Double Duct Sign Microcystic Form
Microcystic Form This CT scan through the head of the pancreas shows large complex mass in the head of the pancreas, associated with an adrenal mass, and multiple masses in the spleen. These findings are consistent with metastatic carcinoma. The patient had a known primary carcinoma of the lung. 20644 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the head of the pancreas shows large complex mass in the head of the pancreas, associated with an adrenal mass, and multiple masses in the spleen. These findings are consistent with metastatic carcinoma. The patient had a known primary carcinoma of the lung. 20644 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This angiogram shows a hypervascular mass in the right kidney consistent with an RCC(a,b), with extension into the IVC (b,c) A second mass that does not respond to intraarterial epinephrine in the left kidney is consistent with a second RCC (d) A hypervascular mass in the head and uncinate process with secondary portal hypertension from A-V shunting reflects a metastatic RCC to the pancreas (e,f). 40437c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This angiogram shows a hypervascular mass in the right kidney consistent with an RCC(a,b), with extension into the IVC (b,c) A second mass that does not respond to intraarterial epinephrine in the left kidney is consistent with a second RCC (d) A hypervascular mass in the head and uncinate process with secondary portal hypertension from A-V shunting reflects a metastatic RCC to the pancreas (e,f). 40437c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a cystic mass in the pancreatic tail associated with surgical absence of the left kidney, a left adrenal nodule and a cholesterol gall stone. Prior surgery with iatrogenic trauma to the tail of the pancreas is the most likely cause of the pseudocyst. The cystic nature needs to be verified by US. 25055 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the pancreas shows a cystic mass in the pancreatic tail associated with surgical absence of the left kidney, a left adrenal nodule and a cholesterol gall stone. Prior surgery with iatrogenic trauma to the tail of the pancreas is the most likely cause of the pseudocyst. The cystic nature needs to be verified by US. 25055 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a cystic mass in the pancreatic tail associated with thickened gastrolienal ligament and ascites. This case represents transperitoneal spread of a known pancreatic carcinoma. Metastatic nodules are also noted in the liver. 20114 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the pancreas shows a cystic mass in the pancreatic tail associated with thickened gastrolienal ligament and ascites. This case represents transperitoneal spread of a known pancreatic carcinoma. Metastatic nodules are also noted in the liver. 20114 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD The CTscan through the head of the pancreas is of a 75 year old female with abdominal discomfort. There is a multiloculated cystic mass in the head of the pancreas. The age sex, appearance, and location make a serous cystadenoma most likely. 40585 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
The CTscan through the head of the pancreas is of a 75 year old female with abdominal discomfort. There is a multiloculated cystic mass in the head of the pancreas. The age sex, appearance, and location make a serous cystadenoma most likely. 40585 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a hypodense mass in the pancreatic head, associated with a central dystrophic calcification and a dilated pancreatic duct. These findings are consistent with a cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the dilated duct. The calcifications in the spleen are granulomatous in origin. 19394c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the pancreas shows a hypodense mass in the pancreatic head, associated with a central dystrophic calcification and a dilated pancreatic duct. These findings are consistent with a cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the dilated duct. The calcifications in the spleen are granulomatous in origin. 19394c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a complex cystic mass with dense peripheral dystrophic calcification in the tail of the pancreas. Associated findings include portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and ascites. These findings are consistent with a cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the PVT. An expanded version of this case appears below. 40712 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the pancreas shows a complex cystic mass with dense peripheral dystrophic calcification in the tail of the pancreas. Associated findings include portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and ascites. These findings are consistent with a cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the PVT. An expanded version of this case appears below. 40712 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas (a,b,c) shows a complex cystic mass with dense peripheral dystrophic calcification in the tail of the pancreas. Associated findings include portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and ascites. The lesions on the weighted image (d) are dark, and are bright on the T2 weighted image consistent with their cystic nature. The portal vein is bright on the T1 image and bright on T2 consistent with acute thromus.T2 weighted image (e) reflects the hypointense cystic masses These findings are consistent with a a diagnosis of cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the PVT. 40717c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the pancreas (a,b,c) shows a complex cystic mass with dense peripheral dystrophic calcification in the tail of the pancreas. Associated findings include portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and ascites. The lesions on the weighted image (d) are dark, and are bright on the T2 weighted image consistent with their cystic nature. The portal vein is bright on the T1 image and bright on T2 consistent with acute thromus.T2 weighted image (e) reflects the hypointense cystic masses These findings are consistent with a a diagnosis of cystadenoma, and a malignant transformation of a mucinous neoplasm has to be considered in view of the PVT. 40717c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CTscan through the head of the pancreas shows a small complex and heterogeneous mass, with dominant hypodensity. The anatomic differential diagnosis lies between the duct and the parenchyma. An ERCP was performed 18143 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CTscan through the head of the pancreas shows a small complex and heterogeneous mass, with dominant hypodensity. The anatomic differential diagnosis lies between the duct and the parenchyma. An ERCP was performed 18143 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD At ERCP mucoid materal was noted in the ampulla. The lesion identified in the uncinate process on the CT was noted as a nodule in the duct. Associated findings included tubular thin filling defects in the duct of the ody consistent with mucus. A diagnosis of mucinous duct ectasia with a papillary tumor with papillary and mucinous features was made at pathology. 40377 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
At ERCP mucoid materal was noted in the ampulla. The lesion identified in the uncinate process on the CT was noted as a nodule in the duct. Associated findings included tubular thin filling defects in the duct of the ody consistent with mucus. A diagnosis of mucinous duct ectasia with a papillary tumor with papillary and mucinous features was made at pathology. 40377 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a large solid mass with vessels that are seemingly not affected by the mass. Associated findings include the retrocrural adenopathy, an aortocaval node and a small amount of ascites. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of lymphoma. 29945 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the pancreas shows a large solid mass with vessels that are seemingly not affected by the mass. Associated findings include the retrocrural adenopathy, an aortocaval node and a small amount of ascites. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of lymphoma. 29945 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas of a 28 year old female with known malignancy shows a large solid mass with central low density. She carries a diagnosis non Hodgkin’s lymphoma Associated findings include steatosis of the liver. 40425c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the pancreas of a 28 year old female with known malignancy shows a large solid mass with central low density. She carries a diagnosis non Hodgkin’s lymphoma Associated findings include steatosis of the liver. 40425c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows a complex cystic mass with central calcification in the tail of the pancreas associated with complex masses in the left kidney and surgically absent right kidney. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome with a variety of cystic and solid, benign and malignant tumors of the pancreas and kidney. 40463c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the pancreas shows a complex cystic mass with central calcification in the tail of the pancreas associated with complex masses in the left kidney and surgically absent right kidney. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome with a variety of cystic and solid, benign and malignant tumors of the pancreas and kidney. 40463c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD This CT scan through the pancreas shows diffuse heterogeneous enlargement of the pancreas, and a series of complex cystic and solid masses mass with punctate calcifications throughout the whole pancreas. Associated findings include a solid mass in the left kidney. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome with a variety of cystic and solid, benign and malignant tumors of the pancreas 40531 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
This CT scan through the pancreas shows diffuse heterogeneous enlargement of the pancreas, and a series of complex cystic and solid masses mass with punctate calcifications throughout the whole pancreas. Associated findings include a solid mass in the left kidney. These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of von Hippel-Lindau syndrome with a variety of cystic and solid, benign and malignant tumors of the pancreas 40531 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD The first image of this series (a), reveals a colon cut off sign and is associated with a mild degree of induration around the pancreas best seen in c. The pancreas itself is enlarged and heterogeneous with a few small complex structures that are too small to resolve, seen best in b and c. A large lipoma is seen in the head of the pancreas in e. The right kidney has a fatty mass in its upper pole consistent with an angiomyolipoma. The overall picture suggests a diagnosis of von Hippel–Lindau syndrome. 40200c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
The first image of this series (a), reveals a colon cut off sign and is associated with a mild degree of induration around the pancreas best seen in c. The pancreas itself is enlarged and heterogeneous with a few small complex structures that are too small to resolve, seen best in b and c. A large lipoma is seen in the head of the pancreas in e. The right kidney has a fatty mass in its upper pole consistent with an angiomyolipoma. The overall picture suggests a diagnosis of von Hippel–Lindau syndrome. 40200c01 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD